
|
Schneider Research Group |
|
Engineering Cell Dynamics |
|
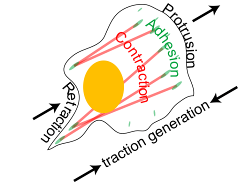
Adhesion and Cytoskeleton Dynamics |
|
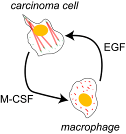
Cancer Cell-Immune Cell Paracrine Interactions |

|
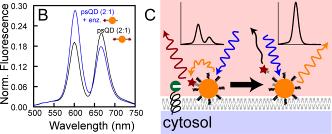
Coincidence Detectors for Cancer Diagnostics |
|
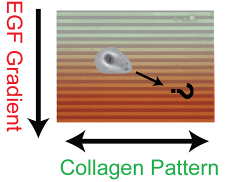
Engineering Multi-cue Migrational Environments |
|
Coincidence Detectors for Cancer Diagnostics: |
|
Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive malignancy refractory to surgical excision and available medical treatments resulting in death within 5 years for 94% of diagnosed patients. Two reasons drive the poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. First, this cancer has not seen decreases in mortality rates like those realized in breast and colon cancer because of a lack of tools to detect pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) before or during the early stages of invasion. Second, this cancer results in difficult removal of all invasive cancerous tissue during surgery, allowing for redevelopment of the tumor. These challenges require a detection strategy specific to pre-invasive cancerous tissue. Nanoparticles provide an ideal detection platform on which to engineer this required specificity. There has been extensive work done to detect cancer using nanoparticles that merely target cancer cells. These have been largely unsuccessful at generating specific localization because these targeted nanoparticles often bind normal tissue, decreasing the specificity of localization. Coincidence detection, the detection of two inputs simultaneously resulting in one output, provides an opportunity to overcome issues of specificity. I plan to build a coincidence detector by engineering nanoparticles with the ability to target PDAC cells (input 1) and sense enzymatic activity (input 2) that is upregulated directly before invasion. Specifically, I will use quantum dots (QDs), which are luminescent nanoparticles that can report enzymatic activity through changes in their optical properties. These nanoparticles will eventually be used during intravital imaging for early PDAC detection or during surgery as pathology tools to help surgeons properly excise all invasive cancer tissue. |